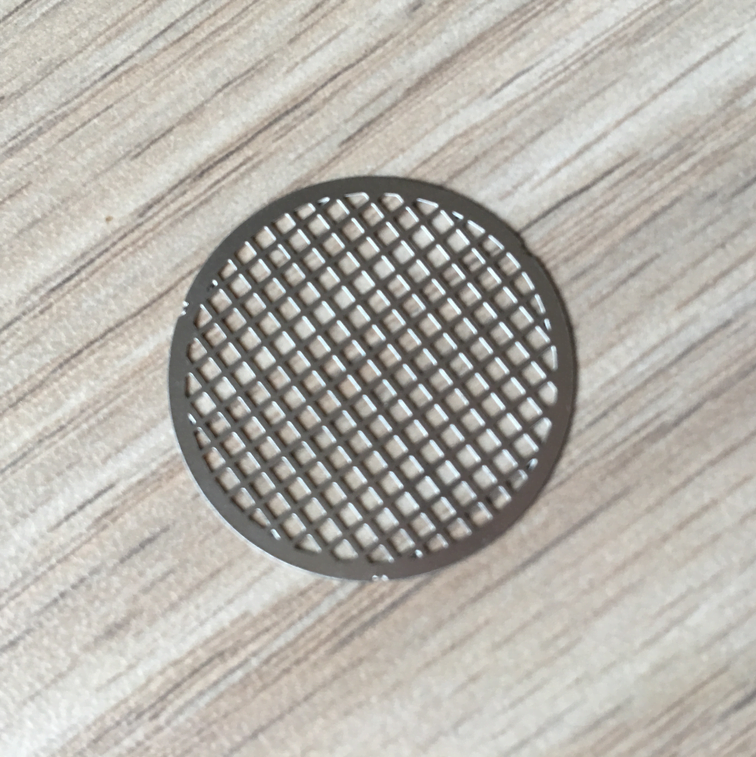
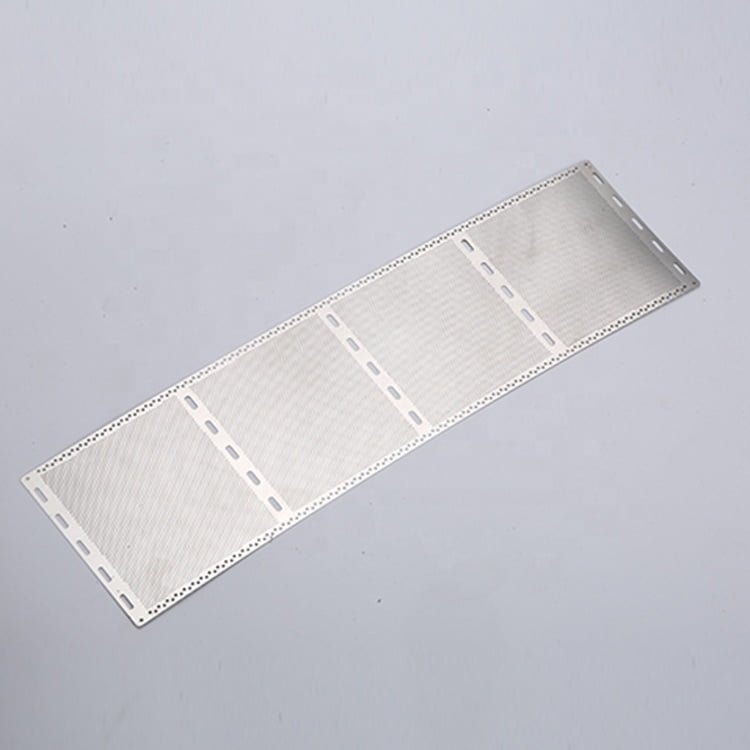
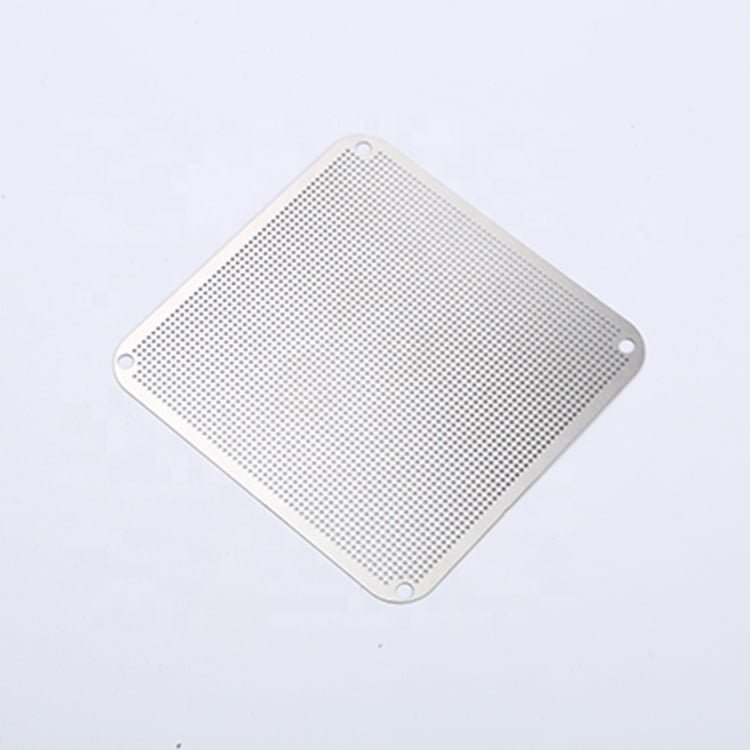
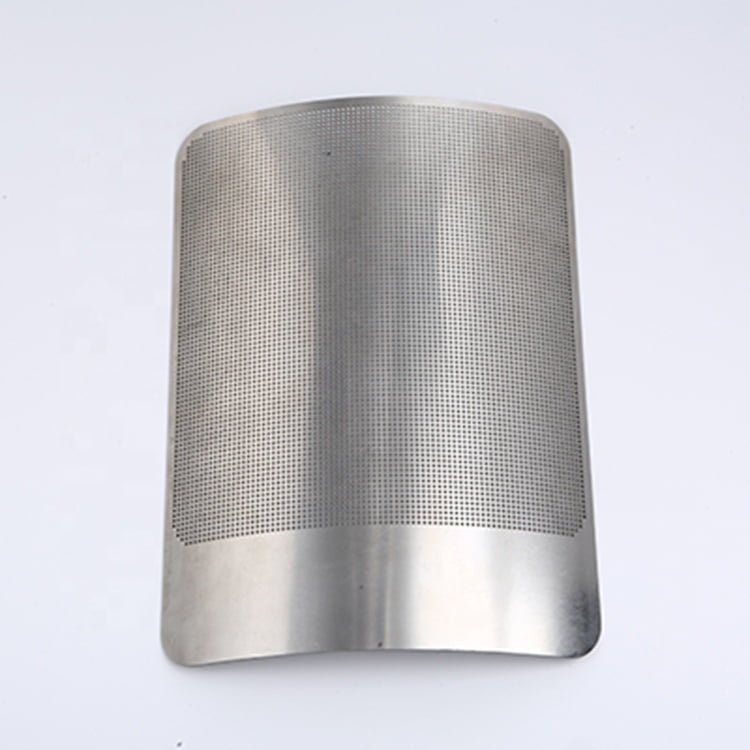
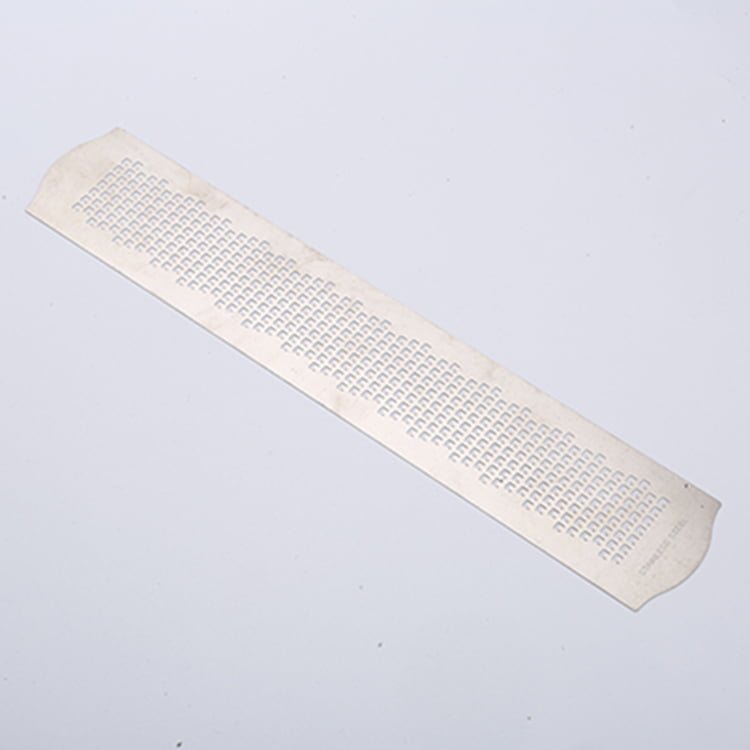
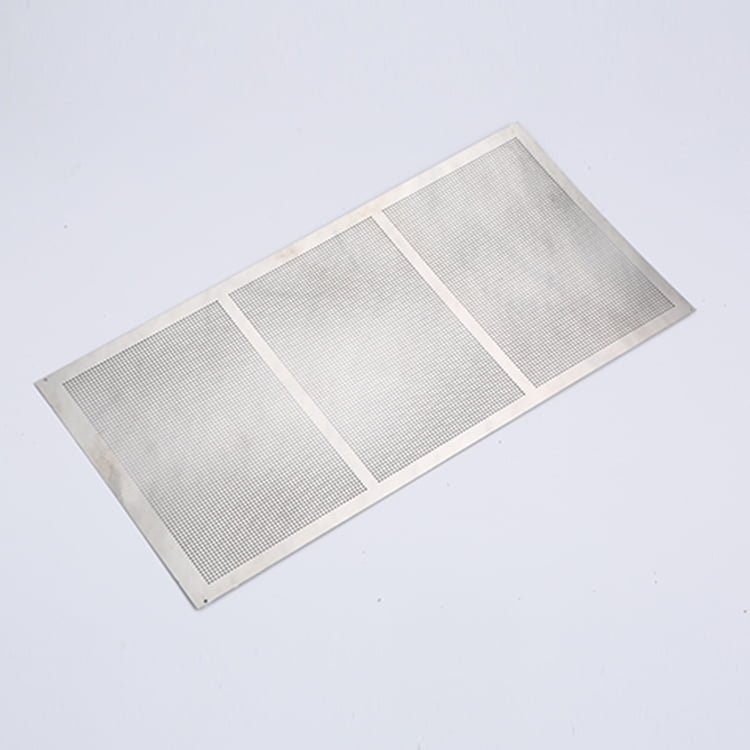
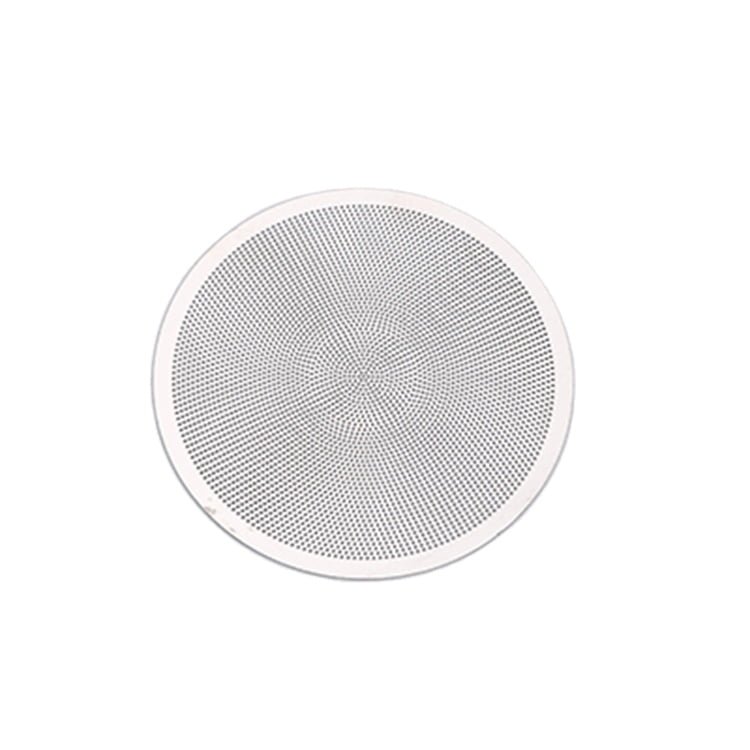
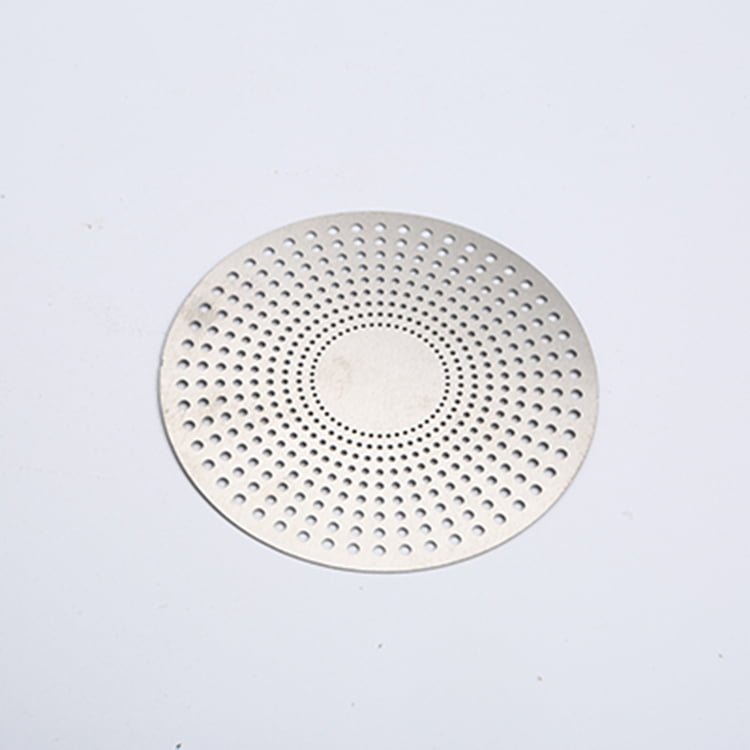
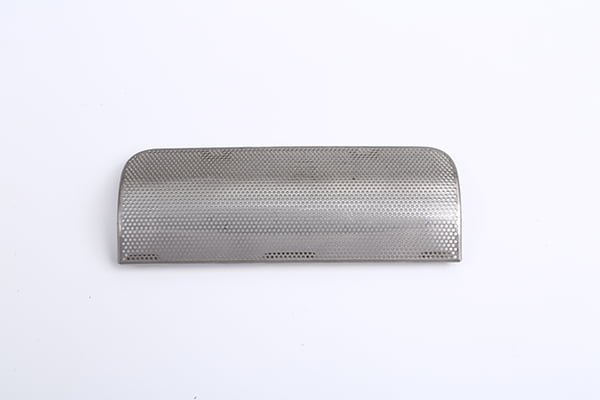
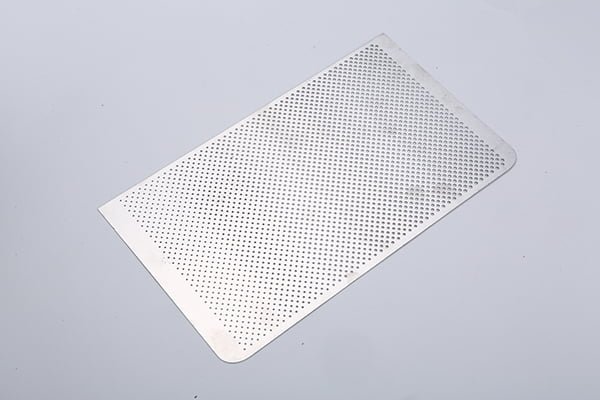
Stainless steel is a versatile and durable material widely used in various industries due to its corrosion resistance and high-strength properties. Achieving precision machining in stainless steel requires careful consideration of the material’s characteristics and the appropriate etching, surface treatment, and electroforming techniques.
[custom_pricing]
How to Etching Stainless Steel?
View or download our Photochemical Metal Etching White Paper How-to Guide
Stainless Steel Types:
Stainless steel is available in several types and alloys, each with its unique properties and applications. Understanding the distinctions is essential before proceeding with any precision machining technique. The most common stainless steel types include:
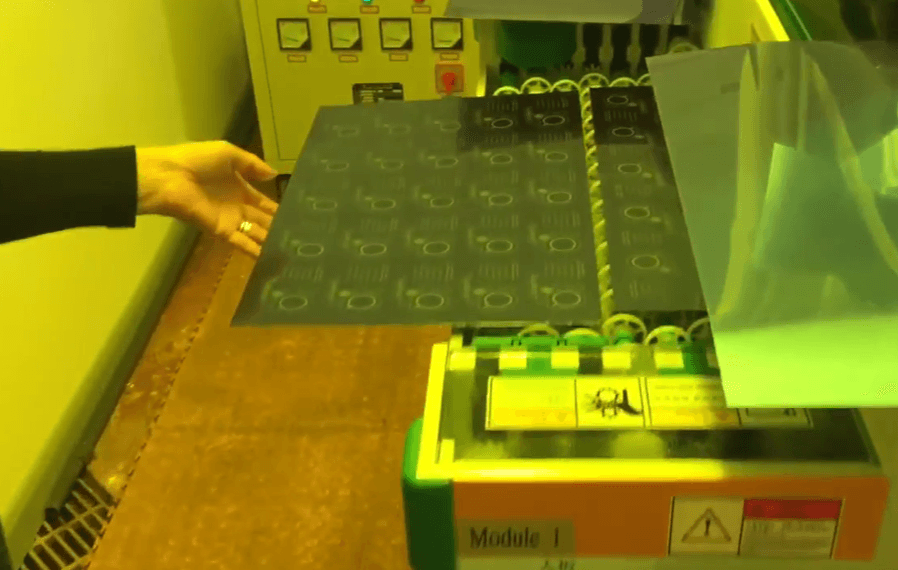
- Austenitic Stainless Steel: Advantages: Offers excellent corrosion resistance and is easy to form and weld. Disadvantages: Lower hardness and limited high-temperature performance.
- Ferritic Stainless Steel: Advantages: Provides good corrosion resistance and exhibits magnetic properties. Disadvantages: Lower toughness and limited weldability.
- Martensitic Stainless Steel: Advantages: Known for high strength, hardness, and wear resistance. Disadvantages: Exhibits lower corrosion resistance and may pose challenges during welding.
- Duplex Stainless Steel: Advantages: Offers an excellent combination of strength and corrosion resistance. Disadvantages: Can be more challenging to process and weld due to its dual-phase microstructure.
Metal Etching Stainless Steel:
Metal etching is a precise process used to selectively remove material from the surface of stainless steel to create intricate patterns, text, or designs. The choice of etchant is crucial, as different stainless steel types require specific chemical etchants for optimal results. Some recommended etchants and their advantages for stainless steel metal etching are:
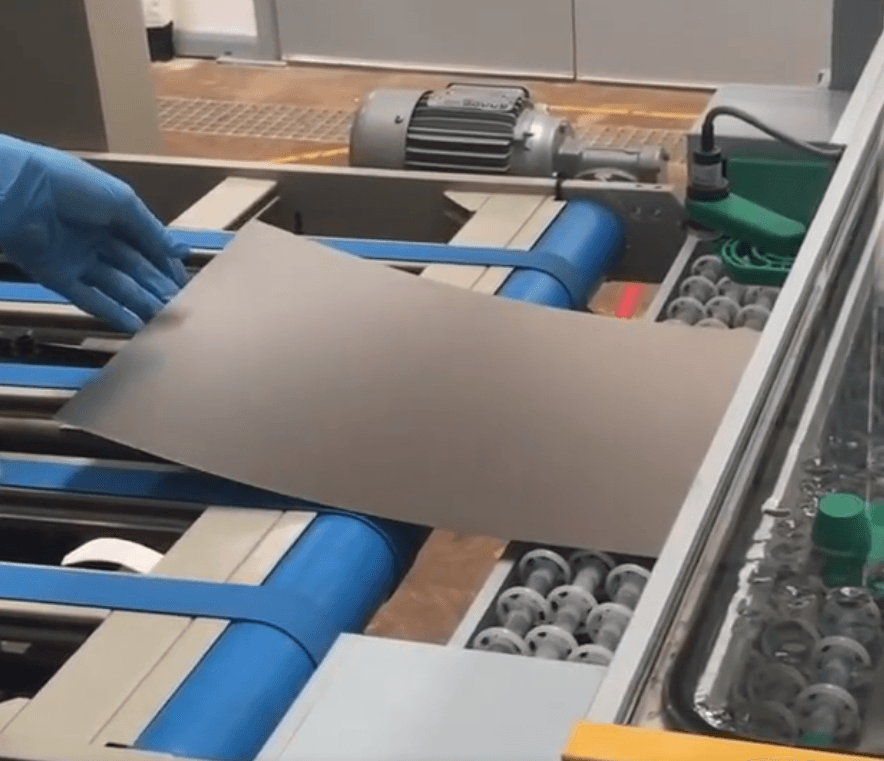

- Ferric Chloride: Advantages: Suitable for austenitic and ferritic stainless steels, providing controlled and uniform etching results. Allows for intricate designs with moderate processing difficulty.
- Nitric Acid: Advantages: Effective on austenitic stainless steels, offering precise etching control and allowing for detailed patterns and textures.
- Hydrochloric Acid: Advantages: Works well on martensitic stainless steels, providing controlled etching and the potential to achieve specific surface designs.
View our metal etching products
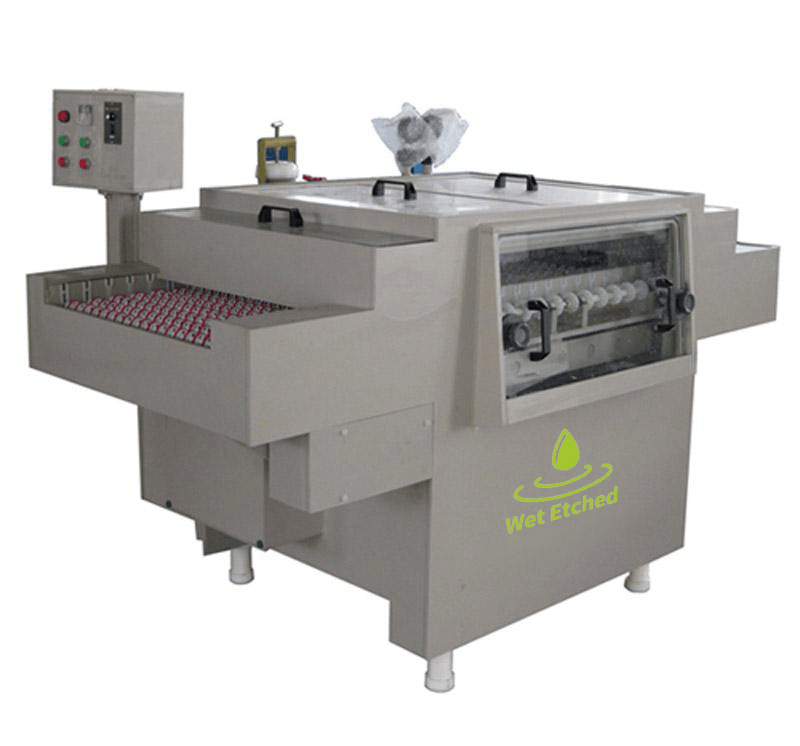
Stainless Steel etching equipment

Selling Price:
$12,000.00
Wet Processing Equipment – Stainless Steel etching machine
The Stainless Steel etching machine is used to spray chemical solution to a copper-clad laminator, aluminum substrate, or stainless steel plate, the exposed copper, aluminum, and stainless steel are etched away, retaining the pattern or circuit covered by the corrosion-proof film, so as to achieve the purpose of making pattern or circuit.
This etching machine is an all-in-one small Stainless Steel etching machine that is easy to install and can be used immediately after powering on.
Photo Etching Stainless Steel:
Photo etching is a precise process used for intricate designs on stainless steel. The choice of material film and temperature control are essential:
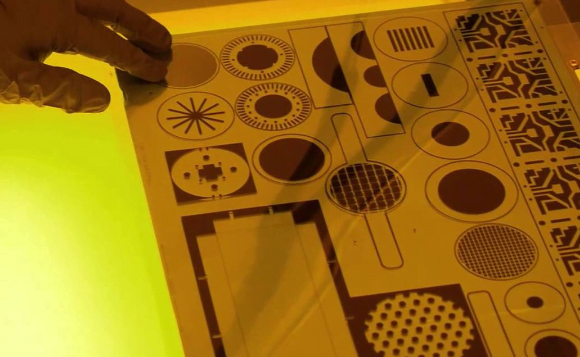
- Material Film: Photomasks made of high-quality polymer films with excellent UV resistance are recommended for precise and detailed etching.
- Temperature Control: Maintain a stable and controlled temperature during the photoresist exposure and development process to ensure accurate pattern transfer.
By understanding the different types of stainless steel and selecting the appropriate etchants, surface treatments, and electroforming techniques, precision machining in stainless steel can be achieved effectively. Metal cleaning and photo etching further enhance the precision and quality of the final products. Following the recommended precautions throughout each process will ensure exceptional results and maintain the integrity of the material. With these insights, manufacturers can confidently produce high-quality stainless steel products tailored to specific applications.
how to etch Stainless Steel?
Etching Stainless Steel Process Guidelines
| Stainless Steel Etching | Etchant | Etching Temperature (°C) | Etching Concentration (%) | Estimated Etch Depth (microns) | Etching Quality |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Etching Stainless Steel | Ferric Chloride | Room temperature | 30% FeCl3 | 5-25 | High-quality (smooth) |
| Etching Austenitic Stainless Steel | Nitric Acid | Room temperature | 10-15% HNO3 | 10-40 | High-quality (smooth) |
| Etching Ferritic Stainless Steel | Hydrochloric Acid | Room temperature | 10-15% HCl | 10-40 | High-quality (smooth) |
| Etching Martensitic Stainless Steel | Ferric Chloride | Room temperature | 30% FeCl3 | 5-25 | High-quality (smooth) |
| Etching Duplex Stainless Steel | Nitric Acid | Room temperature | 10-15% HNO3 | 10-40 | High-quality (smooth) |
| Etching Precipitation-Hardening Stainless Steel | Hydrochloric Acid | Room temperature | 10-15% HCl | 10-40 | High-quality (smooth) |
The values provided are approximate and can vary depending on specific etching conditions, including exposure time and the condition of the stainless steel surface. Always conduct test etches and adjust parameters as needed to achieve your desired results. Additionally, safety precautions should be followed when handling these chemicals.
If you have metal wet etching Stainless Steel needs, please feel free to contact us.
FAQs
[FAQS]
Etching Stainless Steel Samples