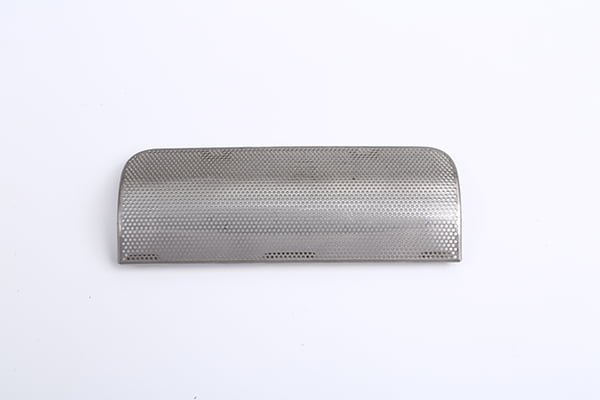
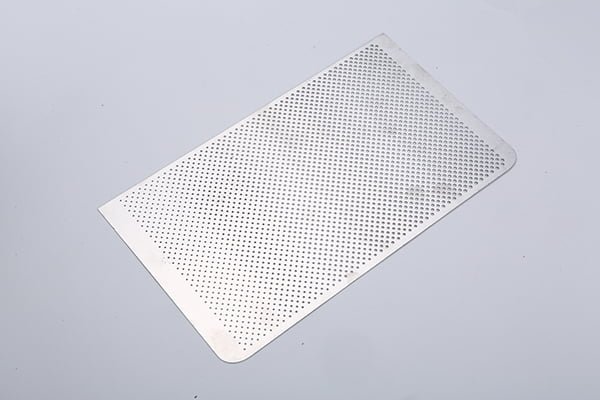
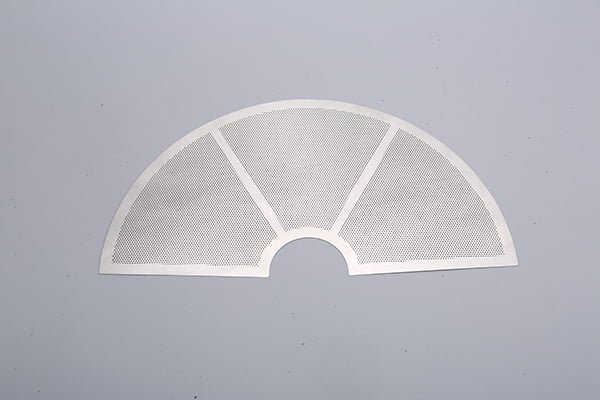
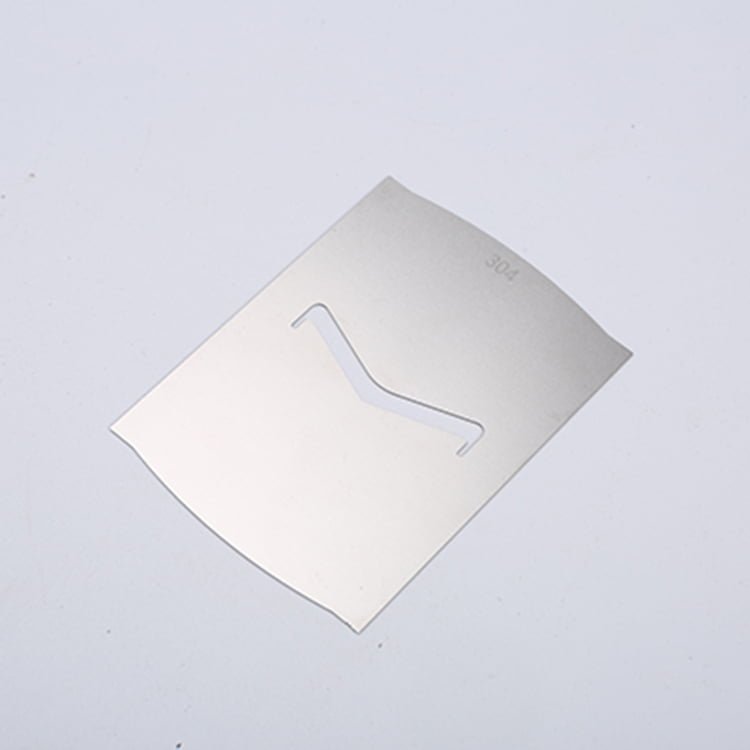
Zirconium, a remarkable refractory metal, boasts exceptional properties that make it a vital material in various industries, including aerospace, nuclear, and chemical processing.
Our Packages
- From 1000pcs
- Samples from 100pcs
- Approx. 30 days (may vary depending on the difficulty of the drawing)
View our Zirconiumetching production facility
Types of Zirconium and Alloys: Advantages and Disadvantages in Wet Processing
Zirconium occurs in various forms, and alloying it with other elements can enhance specific attributes. Let’s analyze the advantages and disadvantages of each alloy for wet processing:

- Pure Zirconium: Advantages include excellent corrosion resistance and biocompatibility, making it ideal for medical implants and chemical processing equipment. Its high ductility, however, can pose challenges during certain etching processes.
- Zirconium-Tin (Zr-Sn): This alloy offers improved mechanical properties and reduced neutron capture cross-section, making it suitable for nuclear reactor applications. Careful consideration is required during etching to avoid surface damage.
- Zirconium-Niobium (Zr-Nb): The addition of Niobium enhances mechanical strength and corrosion resistance. It is commonly used in aerospace and chemical processing, but etching may require specialized techniques to maintain material integrity.
Metal Etching Zirconium
Metal etching in the wet processing process involves the use of metal etching machines. The choice of etchant, such as Hydrofluoric Acid (HF), Ferric Chloride Etchant, or Cupric Chloride Etchant, impacts the processing difficulty. Let’s explore the key aspects of metal etching for zirconium:

- Etching Difficulty: Zirconium’s resistance to corrosion poses challenges during etching. Hydrofluoric Acid (HF) is highly corrosive and requires careful handling to achieve precise etching, while Ferric Chloride Etchant offers deep and well-defined patterns. Cupric Chloride Etchant provides controlled etching and is commonly used in electronic applications.
- Precautions: Due to the corrosive nature of etchants, strict safety precautions are essential. Proper ventilation, personal protective equipment, and adherence to handling protocols are necessary to prevent exposure to hazardous fumes and chemical burns.
One of the recommended alkaline etchants for etching Zirconium is a solution of Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH). Sodium Hydroxide is a strong base and can effectively etch Zirconium by removing thin layers of the material.
The etching process with Sodium Hydroxide is typically carried out at elevated temperatures to enhance its etching capabilities. The etching rate and selectivity can be controlled by adjusting the concentration of the Sodium Hydroxide solution and the temperature.
It’s important to handle Sodium Hydroxide with care as it is caustic and can cause skin and eye irritation. Proper safety measures, including the use of protective equipment and good ventilation, should be observed when working with Sodium Hydroxide for Zirconium etching.
View our metal etching products
Zirconium etching equipment
Photo Etching Zirconium
Photo etching, also known as chemical milling, offers precise and intricate patterns on zirconium surfaces. The process involves using light-sensitive masks to protect specific areas while etching the exposed regions. Let’s explore the key aspects of photo etching for zirconium:
- Processing Difficulty: Photo etching demands exceptional accuracy and control. The photoresist must be carefully applied and developed to ensure accurate pattern transfer onto the zirconium surface. The use of advanced photolithography techniques and skilled expertise is crucial to achieving the desired precision.
- Precautions: Handling of the photoresist requires a clean and controlled environment to prevent contamination. Careful adherence to processing times and temperatures during developing ensures precise pattern transfer without overetching or underetching.
Etching precision-machined zirconium materials is a highly specialized process that requires a thorough understanding of the different types and alloys of zirconium, as well as the intricacies of electroforming, surface treatment, metal cleansing, and etching techniques. By selecting the most suitable processes and adhering to stringent precautions, manufacturers and engineers can unlock the full potential of zirconium, contributing to innovation and progress in a wide range of industries.
how to etch Zirconium?
Etching Zirconium Process Guidelines
| Metal Alloy | Etchant | Etching Temperature (°C) | Etching Concentration (%) | Estimated Etching Depth (microns) | Etching Quality |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Etching Pure Zirconium | Hydrofluoric Acid (HF) | Room temperature | 5% HF | 10-40 | High-quality (smooth) |
| Etching Zirconium-Tin (Zr-Sn) | Ferric Chloride Etchant | Room temperature | 10% FeCl3 | 10-50 | High-quality (smooth) |
| Etching Zirconium-Niobium (Zr-Nb) | Cupric Chloride Etchant | Room temperature | 10% CuCl2 | 10-50 | High-quality (smooth) |
| Etching Zirconium-Niobium (Zr-Nb) | Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH) | Room temperature | 10-20% NaOH | 10-50 | High-quality (smooth) |
The values provided are approximate and can vary depending on specific etching conditions, including exposure time and the condition of the zirconium or zirconium alloy surface. Always conduct test etches and adjust parameters as needed to achieve your desired results. Additionally, safety precautions should be followed when handling these chemicals, especially in the case of Hydrofluoric Acid.
If you have metal wet etching Zirconium needs, please feel free to contact us.
FAQs
What metals can you use to customize my goods?
- Wet Etching Germanium
- Wet Etching Gallium Nitride (GaN)
- Wet Etching Indium
- Wet Etching Cobalt
- Wet Etching Tungsten
- Wet Etching Stainless Steel
- Wet Etching Aluminum
- Wet Etching Kovar
- Wet Etching Copper
- Wet Etching Steel
- Wet Etching Nickel
- Wet Etching Platinum
- Wet Etching Silver
- Wet Etching Rhodium
- Wet Etching Hafnium
- Wet Etching Vanadium
- Wet Etching Zirconium
- Wet Etching Titanium
- Wet Etching Niobium
- Wet Etching Tantalum
- Wet Etching Molybdenum
- Wet Etching Brass
- Wet Etching Rhenium
How quickly can I get your response?
Within 24 hours.
Will you do 100% inspection before shipping out the orders?
Yes we do.
Can I have prototypes or samples before placing the order?
Samples are always available.
Etching Zirconium Samples