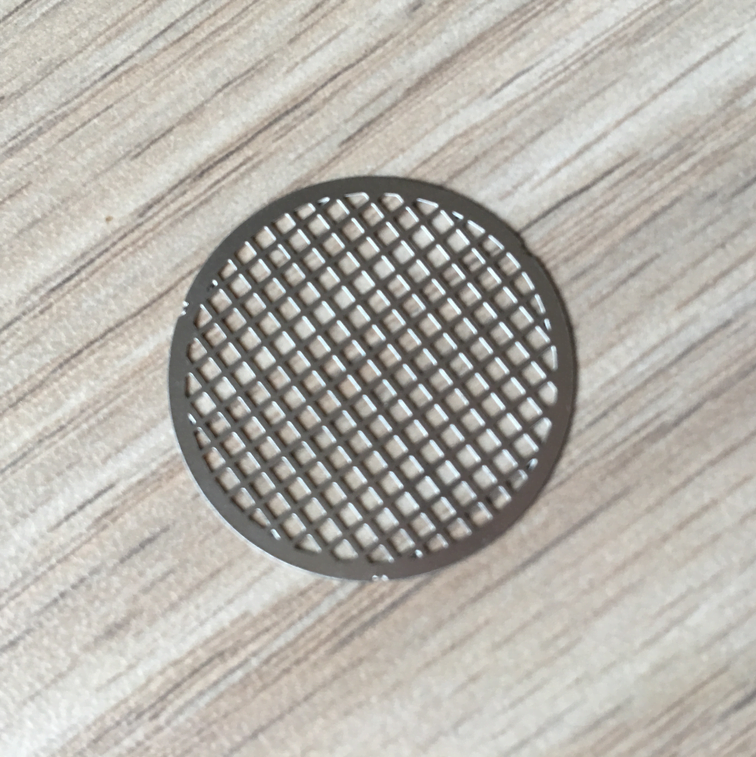
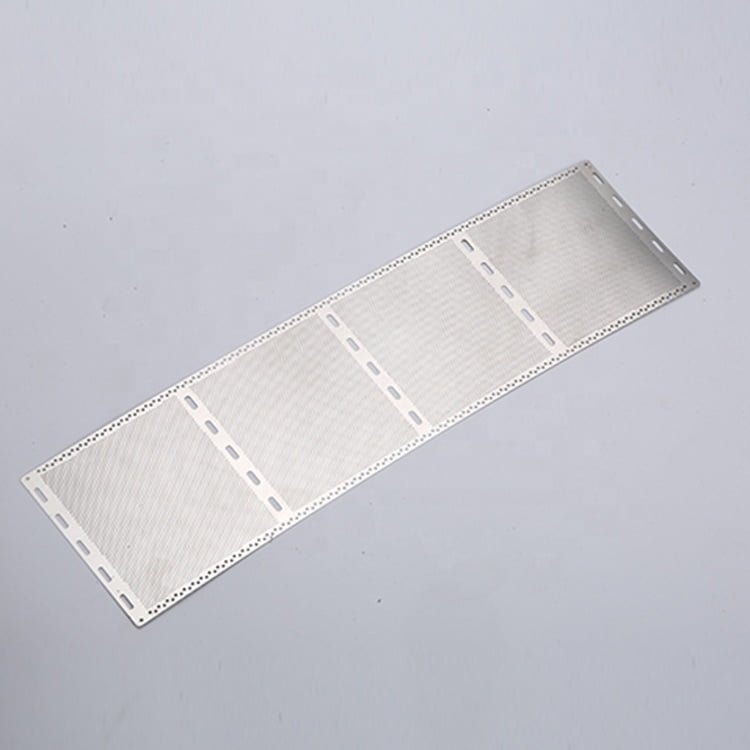
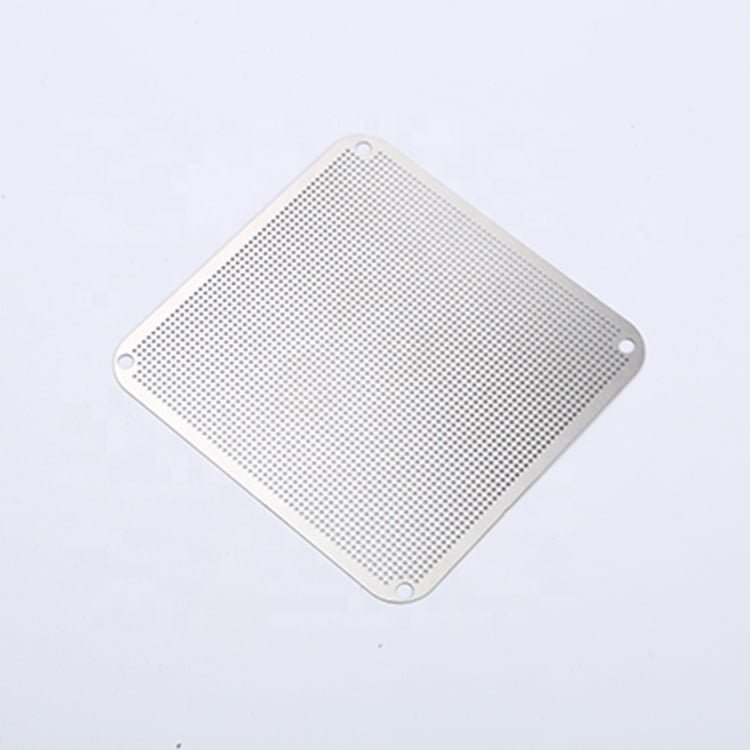
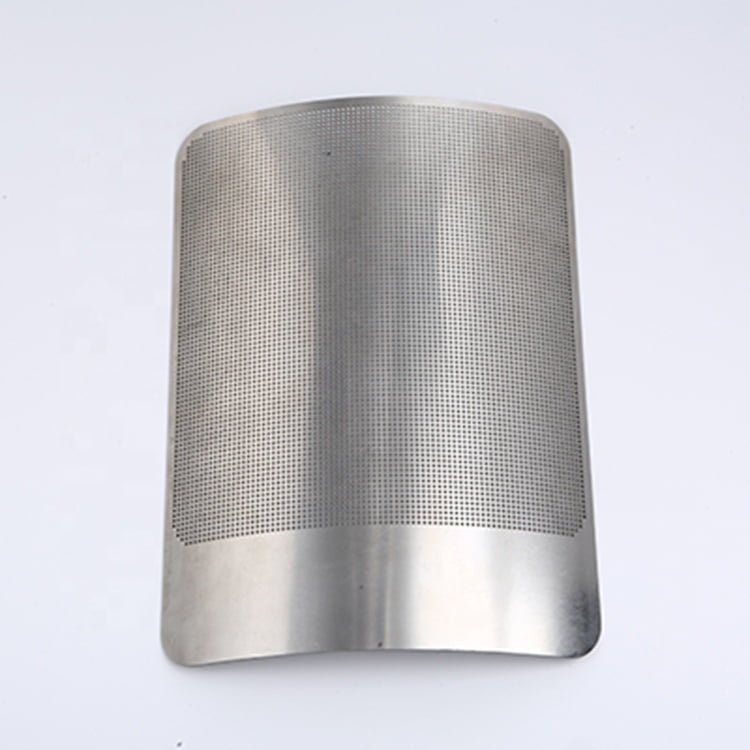
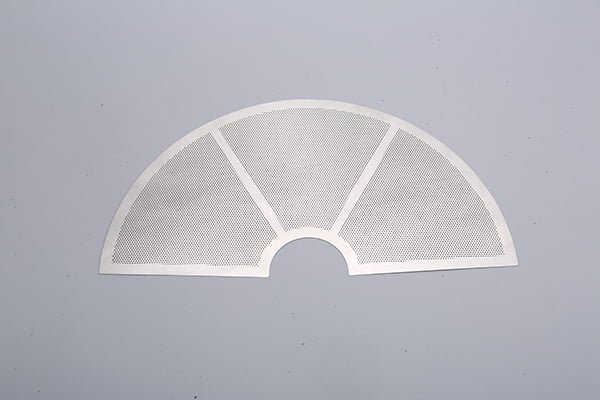
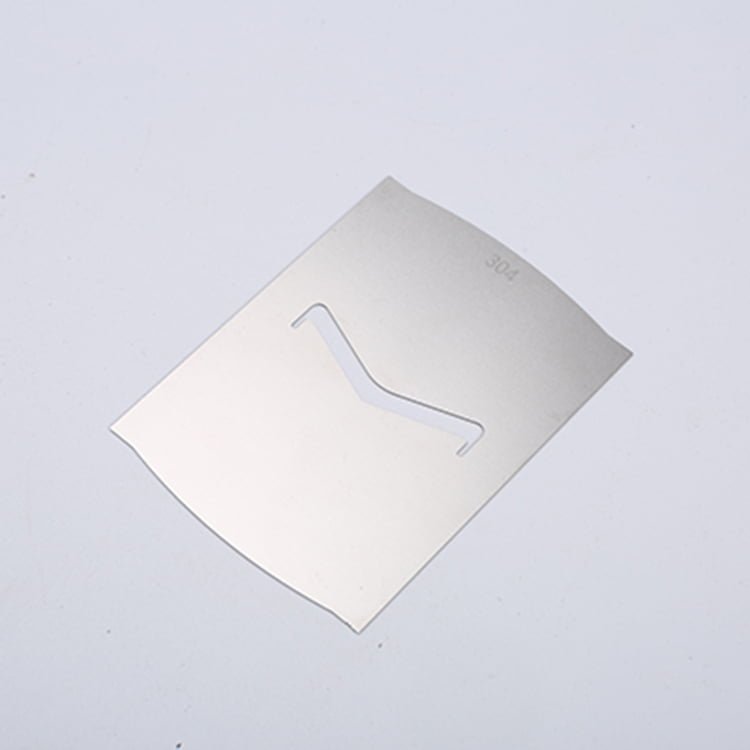
Gallium Nitride (GaN) is a semiconductor material that has gained significant attention in recent years due to its exceptional electronic properties. Its wide bandgap, high electron mobility, and thermal conductivity make it a promising material for high-power and high-frequency electronic devices.
Our Packages
- From 1000pcs
- Samples from 100pcs
- Approx. 30 days (may vary depending on the difficulty of the drawing)
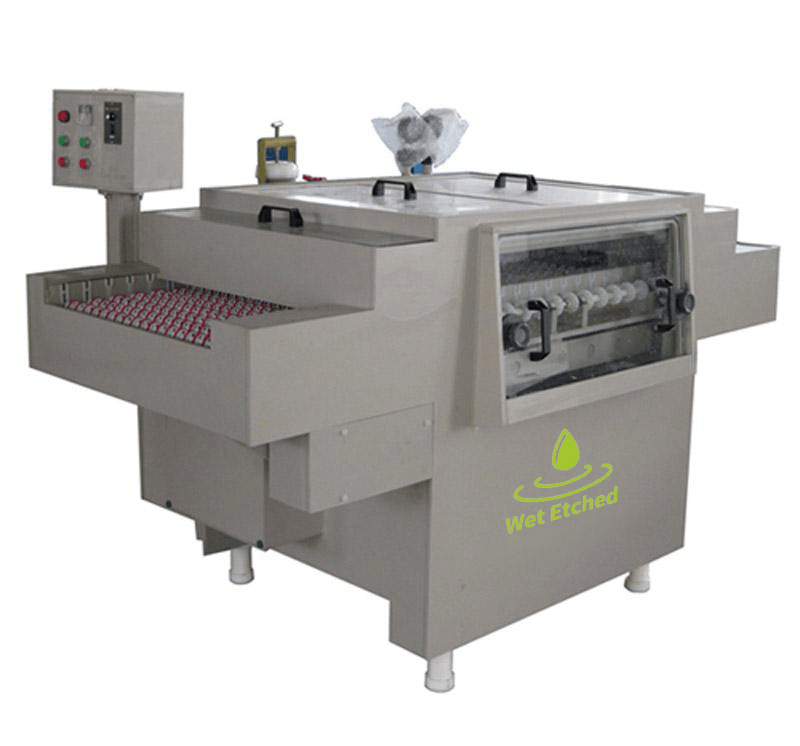
View our GaN etching production facility
Gallium Nitride Characteristics:
Gallium Nitride possesses several key properties that contribute to its growing applications in the semiconductor industry:
- Wide Bandgap: Gallium Nitride has a wide bandgap of approximately 3.4 eV, enabling it to handle high voltages and operate at high temperatures.
- High Electron Mobility: GaN exhibits high electron mobility, making it suitable for high-frequency and high-power electronic devices.
- Thermal Conductivity: Gallium Nitride has excellent thermal conductivity, allowing it to dissipate heat efficiently.
- Stability: GaN is chemically stable, providing durability in harsh environments.
Metal Etching Gallium Nitride:
Metal etching is a precise process used to selectively remove material from the surface of Gallium Nitride to create intricate patterns and designs. When etching Gallium Nitride, the choice of etchant is critical for achieving optimal results:
- Inductively Coupled Plasma (ICP) Dry Etching: ICP dry etching is a common method for etching GaN. Gases such as chlorine (Cl2), bromine (Br2), and sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) are used in ICP etching processes to react with GaN, selectively removing material. The choice of gas depends on the specific etch rate and selectivity requirements.
- Reactive Ion Etching (RIE): RIE is another dry etching technique used for GaN. It involves using reactive gases, such as chlorine or fluorine-based compounds, in a low-pressure plasma to etch the GaN surface selectively.
- Plasma Etching: Plasma etching using various gases can be used for precise and controlled etching of GaN. Common gases used include SF6 and O2, which can create a chemically reactive plasma to etch GaN.
- Hot Phosphoric Acid (H3PO4): Hot phosphoric acid can be used for wet etching of GaN. It is a selective etchant that can remove GaN while leaving other materials intact. However, it requires high-temperature conditions and can be corrosive.
- Potassium Hydroxide (KOH): KOH can also be used as a wet etchant for GaN. It’s a more gentle etchant compared to hot phosphoric acid and is often used for slower, isotropic etching.
- Hydrochloric Acid (HCl): Dilute hydrochloric acid solutions can be used for wet etching of GaN under certain conditions. The selectivity and etch rate can be controlled by adjusting the acid concentration and temperature.
- Eutectic Alloy: In some cases, eutectic alloys like gold-gallium (Au-Ga) or gold-indium (Au-In) may be used to selectively bond to GaN, and subsequent removal of the alloy can result in selective etching.
Gan etching equipment
Wet Processing Equipment – Gan etching machine
The Gan etching machine is used to spray chemical solution to a copper-clad laminator, aluminum substrate, or stainless steel plate, the exposed copper, aluminum, and stainless steel are etched away, retaining the pattern or circuit covered by the corrosion-proof film, so as to achieve the purpose of making pattern or circuit.
This etching machine is an all-in-one small Gan etching machine that is easy to install and can be used immediately after powering on.
Photo Etching Gallium Nitride:
Photo etching is a precise process used for intricate designs on Gallium Nitride:
- Material Film: Photomasks made of high-quality polymer films with excellent UV resistance are recommended for precise and detailed etching.
- Temperature Control: Maintain a stable and controlled temperature during the photoresist exposure and development process to ensure accurate pattern transfer.
Gallium Nitride’s exceptional electronic properties make it a promising material for high-power and high-frequency electronic devices. By understanding the etchants, surface treatment methods, electroforming techniques, metal cleaning, and photo etching processes for Gallium Nitride, manufacturers can achieve exceptional results without compromising the material’s integrity. Applying these insights will enable the production of high-quality Gallium Nitride devices with enhanced performance for diverse semiconductor applications.
View our metal etching products
how to etch Gallium Nitride (GaN)?
Etching Gallium Nitride (GaN) Processing Guidelines
| Material | Etchant | Temperature (°C) | Concentration (%) | Estimated Etch Depth (microns) | Etch Quality |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Etching Gallium Nitride | Reactive Ion Etching (RIE) | Room temperature | N/A | Variable depth, controlled by RIE process | High-quality (precise) |
| Etching Gallium Nitride | Hot Phosphoric Acid (H3PO4) | 160-180 | 85% | 1-10 | High-quality (smooth) |
| Etching Gallium Nitride | Potassium Hydroxide (KOH) | 80-100 | 30% | 0.5-5 | High-quality (smooth) |
| Etching Gallium Nitride | Hydrochloric Acid (HCl) | Room temperature | 10% | 1-10 | Moderate-quality (etched) |
Please note that the estimated etch depths and etch quality may vary based on factors such as exposure time, agitation, and the specific etching conditions, particularly in the case of Reactive Ion Etching (RIE). RIE is a specialized process, and the etch depth is controlled differently compared to wet chemical etching. Always conduct test etches and adjust parameters as needed to achieve your desired results. Additionally, safety precautions should be followed when handling these chemicals, particularly the use of appropriate personal protective equipment.
If you have metal wet etching GaN needs, please feel free to contact us.
FAQs
What metals can you use to customize my goods?
- Wet Etching Germanium
- Wet Etching Gallium Nitride (GaN)
- Wet Etching Indium
- Wet Etching Cobalt
- Wet Etching Tungsten
- Wet Etching Stainless Steel
- Wet Etching Aluminum
- Wet Etching Kovar
- Wet Etching Copper
- Wet Etching Steel
- Wet Etching Nickel
- Wet Etching Platinum
- Wet Etching Silver
- Wet Etching Rhodium
- Wet Etching Hafnium
- Wet Etching Vanadium
- Wet Etching Zirconium
- Wet Etching Titanium
- Wet Etching Niobium
- Wet Etching Tantalum
- Wet Etching Molybdenum
- Wet Etching Brass
- Wet Etching Rhenium
How quickly can I get your response?
Within 24 hours.
Will you do 100% inspection before shipping out the orders?
Yes we do.
Can I have prototypes or samples before placing the order?
Samples are always available.
Etching GaN Samples