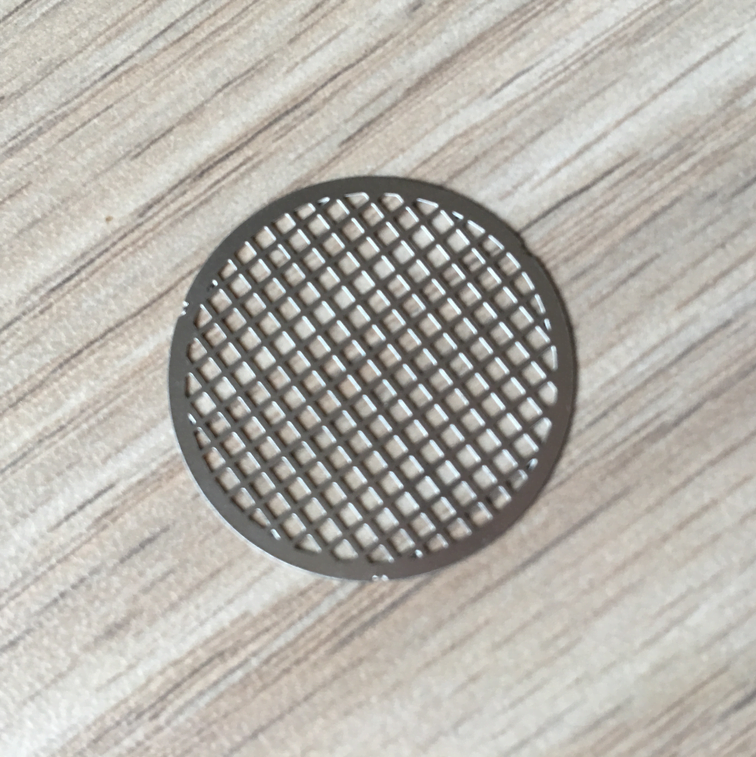
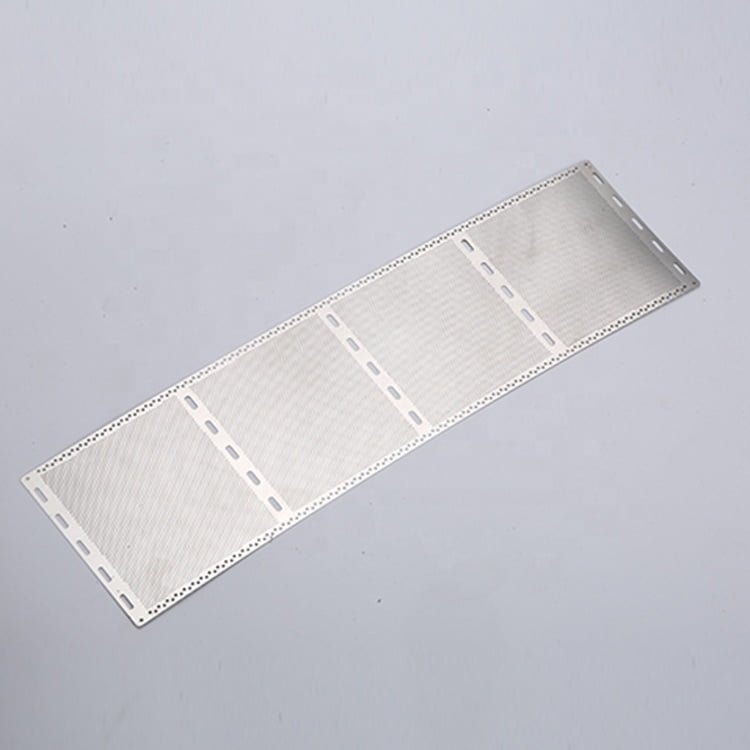
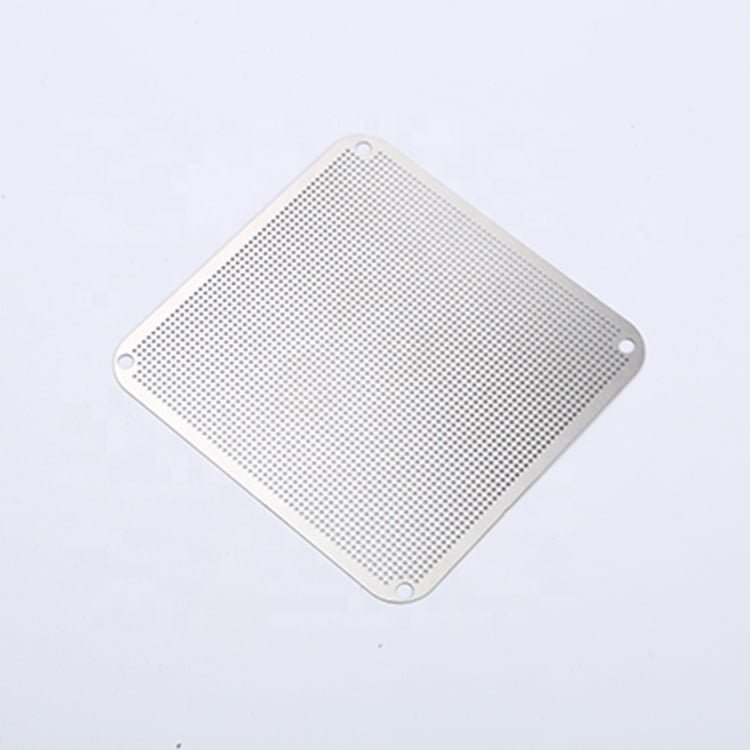
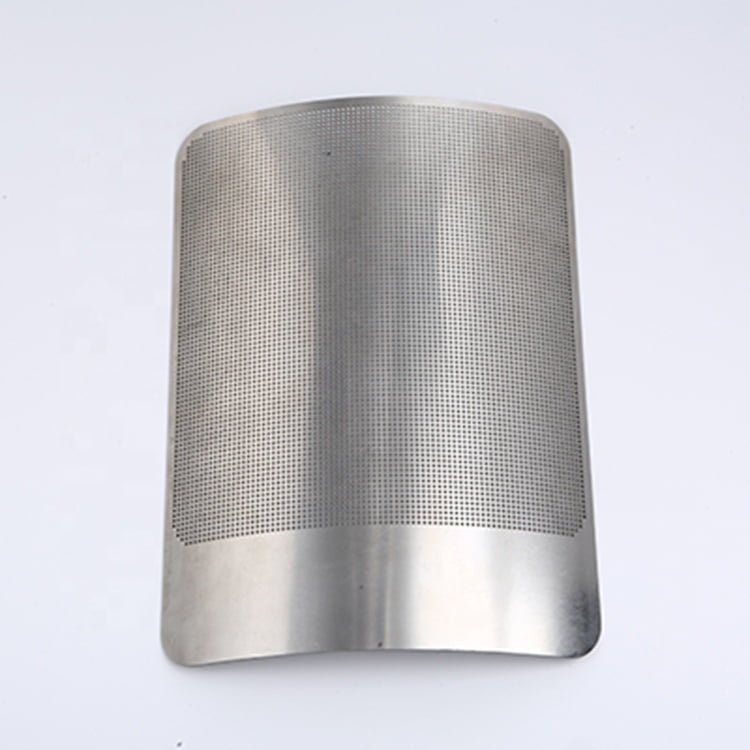
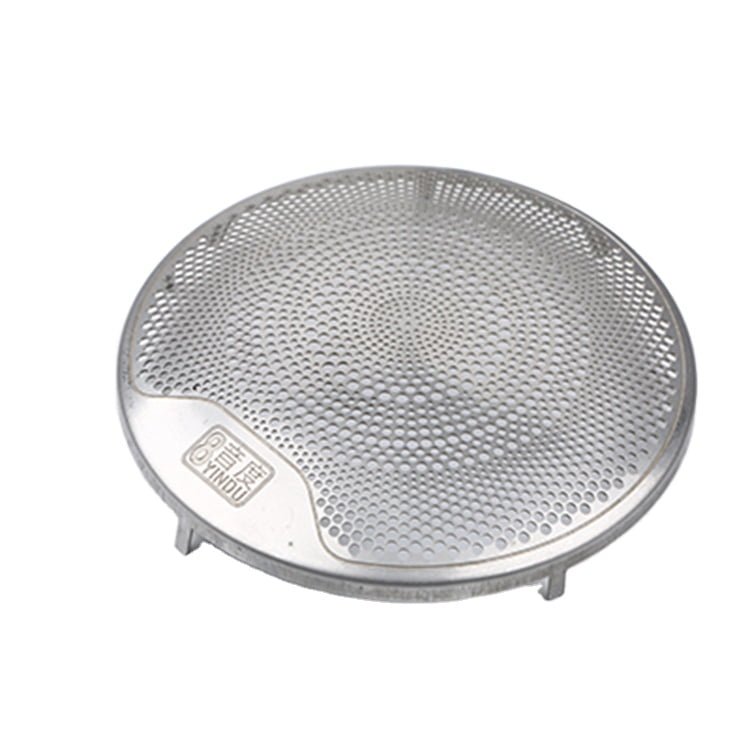
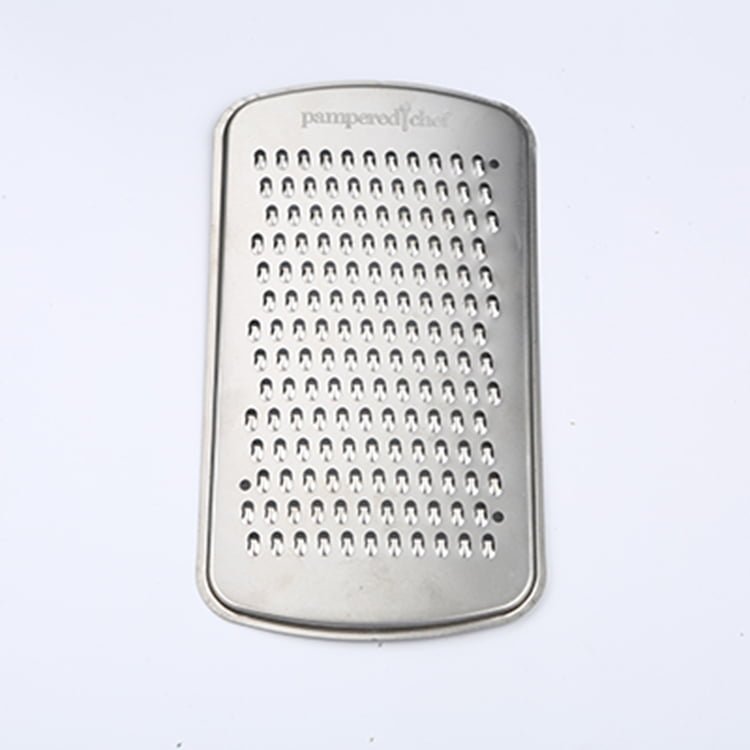
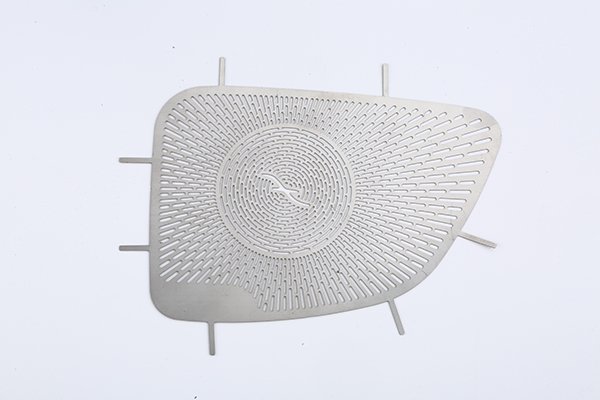
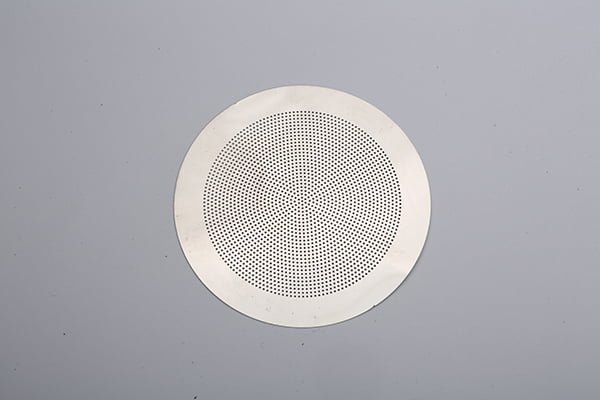
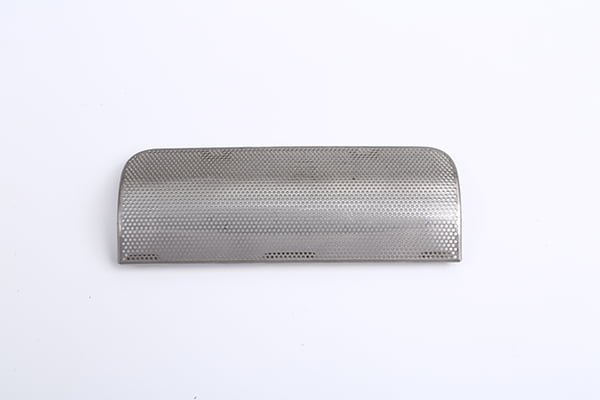
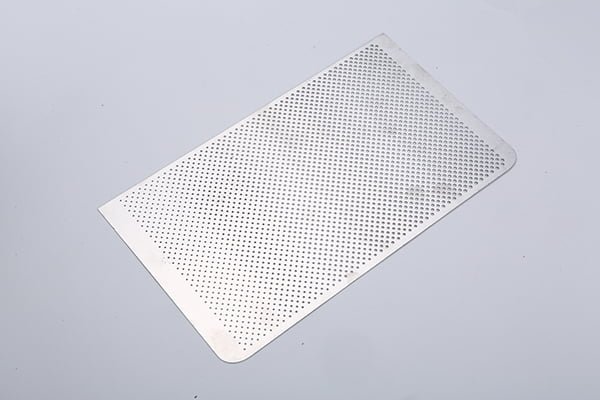
Brass, a versatile and aesthetically pleasing alloy, has been a popular choice in various industries for centuries.
Our Packages
- From 1000pcs
- Samples from 100pcs
- Approx. 30 days (may vary depending on the difficulty of the drawing)
View our Brass etching production facility
Types of Brass and Alloys
Brass comes in various compositions and alloys, each tailored to meet specific requirements. Some common types include:

- Alpha Brass: Containing up to 40% zinc, Alpha Brass is highly malleable and can be easily cold-worked, making it suitable for applications like musical instruments and decorative items.
- Alpha-Beta Brass: With a zinc content of 40-45%, Alpha-Beta Brass exhibits both malleability and increased strength, ideal for applications that demand a balance between formability and durability.
- Beta Brass: Comprising more than 45% zinc, Beta Brass offers exceptional strength and hardness, making it suitable for components requiring high performance, such as springs and fasteners.
Metal Etching Brass
Metal etching is a fundamental process used to shape, pattern, or remove material from Brass surfaces. Wet etching, using etching machines, is commonly employed for this purpose. The selection of a suitable etchant depends on the desired results and the processing difficulty involved. Common etchants for Brass include:
- Hydrofluoric Acid (HF): A highly corrosive etchant suitable for removing thin layers of Brass and achieving precise etching. Safety precautions should be followed during handling.
- Ferric Chloride Etchant: Widely used for etching Brass due to its ability to create deep and well-defined patterns. Proper disposal and handling are essential due to its corrosive nature.
- Cupric Chloride Etchant: Offers controlled etching and is commonly used in electronic applications. Proper ventilation is necessary as it releases hazardous fumes.
there are several recommended alkaline etchants for etching Brass. Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc, and its etching process typically involves using alkaline solutions. Here are some commonly used alkaline etchants for etching Brass:
- Ammonium Persulfate (NH4)2S2O8: Ammonium persulfate is a widely used alkaline etchant for Brass. It is relatively safe to handle compared to some other etchants.
- Cupric Chloride (CuCl2): Cupric chloride is an effective alkaline etchant for Brass, providing controlled and precise etching.
- Ferric Chloride (FeCl3): While Ferric chloride is more commonly used as an acidic etchant for copper, it can also be used as an alkaline etchant for Brass when mixed with suitable alkaline additives.
- Alkaline Cyanide Solutions: Alkaline cyanide solutions can be used for etching Brass, but they are highly toxic and require careful handling and disposal. Therefore, extreme caution should be exercised when using cyanide-based etchants.
- Alkaline Electrolytes: Some alkaline electrolytes can also be used for etching Brass, particularly in electrochemical etching processes.
Brass etching equipment
Photo Etching Brass
Photo etching, also known as chemical milling, offers precise and intricate patterns on Brass surfaces. The process involves using light-sensitive masks to protect specific areas while etching the exposed regions. The difficulty lies in handling the photoresist and ensuring accurate pattern transfer. Skilled expertise is crucial to achieve the desired precision in the final product.
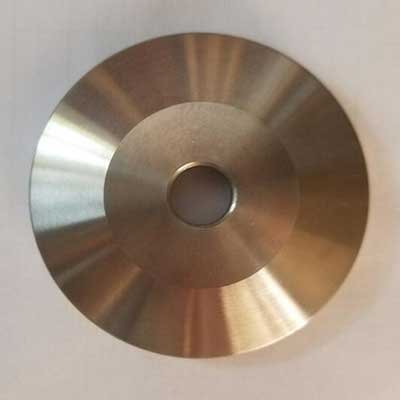

The beauty and versatility of precision-processed metal Brass materials have made them an integral part of numerous industries. Understanding the different types and alloys of Brass, along with exploring the complexities of electroforming, surface treatment, metal cleansing, and etching processes, allows manufacturers and engineers to harness the full potential of Brass. By selecting the most suitable processes and adhering to necessary precautions, Brass materials can continue to contribute to cutting-edge technology, aesthetics, and innovation across various domains.
View our metal etching products
how to etch Brass?
Etching Brass Process Guidelines
| Brass Type | Etchant | Etching Temperature (°C) | Etching Concentration (%) | Estimated Etching Depth (microns) | Etching Quality |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Etching Alpha Brass | Hydrofluoric Acid (HF) | Room temperature | 5% HF | 10-40 | High-quality (smooth) |
| Etching Alpha-Beta Brass | Ferric Chloride Etchant | Room temperature | 10% FeCl3 | 10-50 | High-quality (smooth) |
| Etching Beta Brass | Cupric Chloride Etchant | Room temperature | 10% CuCl2 | 10-50 | High-quality (smooth) |
| Etching Alpha Brass | Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH) | Room temperature | 10-20% NaOH | 10-50 | High-quality (smooth) |
| Etching Alpha-Beta Brass | Ammonium Persulfate ((NH4)2S2O8) | Room temperature | 10% APS | 10-50 | High-quality (smooth) |
| Etching Beta Brass | Ferric Chloride (FeCl3) | Room temperature | 10% FeCl3 | 10-50 | High-quality (smooth) |
| Etching Alpha Brass | Alkaline Cyanide Solutions | Room temperature | Varies | 10-50 | High-quality (smooth) |
| Etching Alpha-Beta Brass | Alkaline Electrolytes | Room temperature | Varies | 10-50 | High-quality (smooth) |
The values provided are approximate and can vary depending on specific etching conditions, including exposure time and the condition of the brass surface. Always conduct test etches and adjust parameters as needed to achieve your desired results. Additionally, safety precautions should be followed when handling these chemicals, especially in the case of Hydrofluoric Acid and cyanide solutions.
If you have metal wet etching Brass needs, please feel free to contact us.
FAQs
What metals can you use to customize my goods?
- Wet Etching Germanium
- Wet Etching Gallium Nitride (GaN)
- Wet Etching Indium
- Wet Etching Cobalt
- Wet Etching Tungsten
- Wet Etching Stainless Steel
- Wet Etching Aluminum
- Wet Etching Kovar
- Wet Etching Copper
- Wet Etching Steel
- Wet Etching Nickel
- Wet Etching Platinum
- Wet Etching Silver
- Wet Etching Rhodium
- Wet Etching Hafnium
- Wet Etching Vanadium
- Wet Etching Zirconium
- Wet Etching Titanium
- Wet Etching Niobium
- Wet Etching Tantalum
- Wet Etching Molybdenum
- Wet Etching Brass
- Wet Etching Rhenium
How quickly can I get your response?
Within 24 hours.
Will you do 100% inspection before shipping out the orders?
Yes we do.
Can I have prototypes or samples before placing the order?
Samples are always available.
Etching Brass Samples