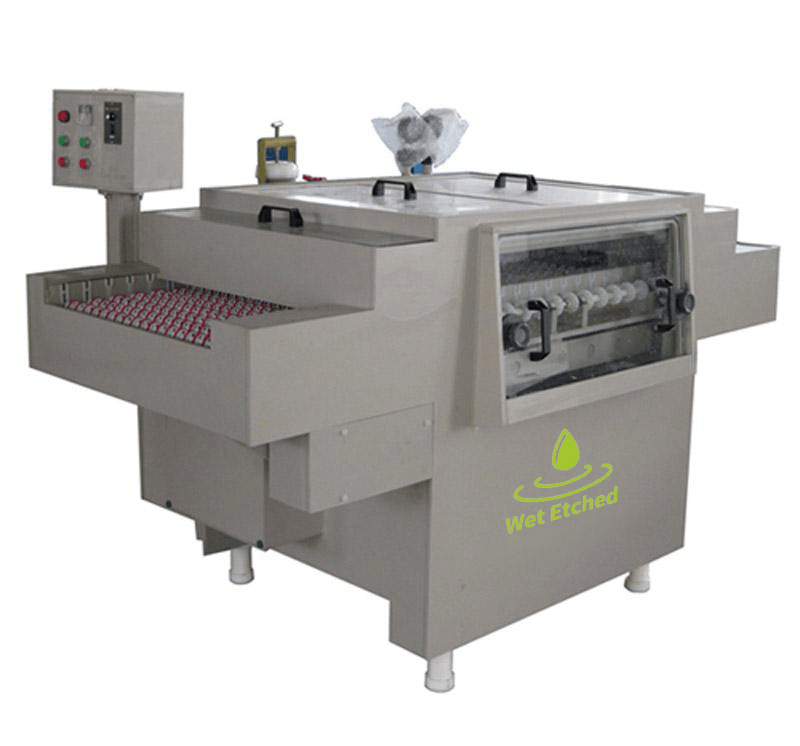

Wet chemical acid etching machines are a powerful and versatile tool for manufacturing high-precision components and designs. With the ability to handle a wide range of materials, create intricate patterns, and maintain high production efficiency, these machines are widely used in industries such as electronics, automotive, jewelry, and more. Understanding how wet chemical etching works, its components, and its advantages can help businesses make informed decisions about incorporating this technology into their operations for improved quality, speed, and cost-effectiveness.
What is Wet Chemical Acid Etching?
Wet chemical acid etching is a precise, cost-effective process used to remove material from the surface of metals and other substrates, leaving behind intricate designs or patterns. It’s commonly used in a variety of industries, including electronics, automotive, jewelry, and manufacturing, to create finely detailed components, circuit boards, and decorative finishes.
The process involves applying a photoresist coating to the material’s surface, exposing the desired design through light, and then chemically etching away the exposed areas. The etching solution, typically an acidic substance, reacts with the exposed metal to create the pattern. This allows manufacturers to achieve high-precision designs with intricate features, which is difficult to achieve using mechanical methods.
In contrast to laser etching or mechanical milling, wet chemical etching is often preferred for high-volume production and applications that require fine, complex patterns.
Components of a Wet Chemical Etching Machine
A wet chemical acid etching machine consists of several key components that work together to ensure precision, efficiency, and safety during the etching process. These components include:
- Photoresist Unit: This component applies a light-sensitive coating to the material’s surface. After exposure to UV light through a mask or stencil, the photoresist hardens in the desired pattern, while the unexposed areas remain soft.
- Etching Bath: The etching bath is where the chemical etching solution is held. This solution, typically an acidic mixture, reacts with the exposed metal to remove it and create the desired pattern.
- Heating System: Many wet etching machines incorporate heating elements to maintain the optimal temperature for etching, which helps speed up the chemical reaction and ensures uniform etching.
- Filtration System: This system filters the etching solution to remove contaminants and particles that could clog the nozzles or affect the etching quality.
- Rinsing and Drying Equipment: After the etching process, the material is rinsed to remove any remaining chemicals and dried before it’s handled or further processed.
Each component plays a critical role in ensuring that the wet etching process is efficient, precise, and consistent.
How Wet Chemical Etching Works
The wet chemical etching process can be broken down into several key stages:
- Preparation and Photoresist Application: The material is cleaned and prepped, and a photoresist coating is applied to its surface. The photoresist is a light-sensitive substance that will protect certain areas of the material from the etching solution.
- Exposure and Development: The material is exposed to ultraviolet (UV) light through a photomask that carries the design pattern. The exposed areas of the photoresist harden, while the unexposed areas are washed away during development, revealing the underlying material in the desired pattern.
- Etching: The material is submerged in an etching bath, which contains a chemical solution designed to react with the exposed areas of the material, removing the metal. The areas covered by the hardened photoresist remain unaffected by the etchant.
- Post-Etching: After etching, the material is rinsed to remove any remaining chemicals, then dried. If necessary, additional processes such as stripping the photoresist are performed to clean up the final design.
This process is highly controlled, allowing manufacturers to produce designs with intricate features and fine details down to micrometer precision. The result is a clean, precise etching with minimal waste and highly accurate outcomes.
Key Advantages of Wet Chemical Etching Machines
Wet chemical etching offers several significant advantages that make it a preferred method for many manufacturers:
- High Precision: Wet etching machines can achieve micron-level precision, making them ideal for applications that require fine details, such as PCB production, jewelry, or fine metalworking.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Compared to other etching methods, wet chemical etching is relatively inexpensive, especially for high-volume production. The chemicals used are often reusable, which reduces material costs.
- Complexity: Wet etching allows for the creation of intricate, complex patterns that would be difficult or impossible to achieve using other methods like laser etching or mechanical milling.
- Scalability: Wet chemical etching is ideal for high-volume production due to its ability to process large batches of materials quickly and consistently.
- Low Environmental Impact: When managed properly, wet chemical etching has a low environmental impact, as the chemicals used in the process can be recycled and treated to minimize waste.
These benefits make wet chemical etching a versatile and popular choice across many industries.
Industries and Applications for Wet Chemical Etching
Wet chemical etching is used across a wide range of industries, offering applications for both functional and decorative purposes. Some of the most common industries and their applications include:
- Electronics: Wet etching is widely used in PCB manufacturing to create circuit patterns on copper-clad boards. It’s also used in the production of MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems) devices and semiconductor components.
- Automotive: Wet chemical etching is used to create components like sensors, gears, and decorative finishes for automotive parts.
- Jewelry: Etching is used in jewelry making to create intricate patterns on metals like gold, silver, and brass.
- Aerospace: Wet etching is used to produce precision components for aircraft, satellites, and other aerospace applications.
- Medical Devices: The process is used to create fine details in medical devices, such as stents and implants, that require high levels of precision and biocompatibility.
Wet chemical etching is essential in industries where high precision, cost-efficiency, and scalability are key factors for success.
