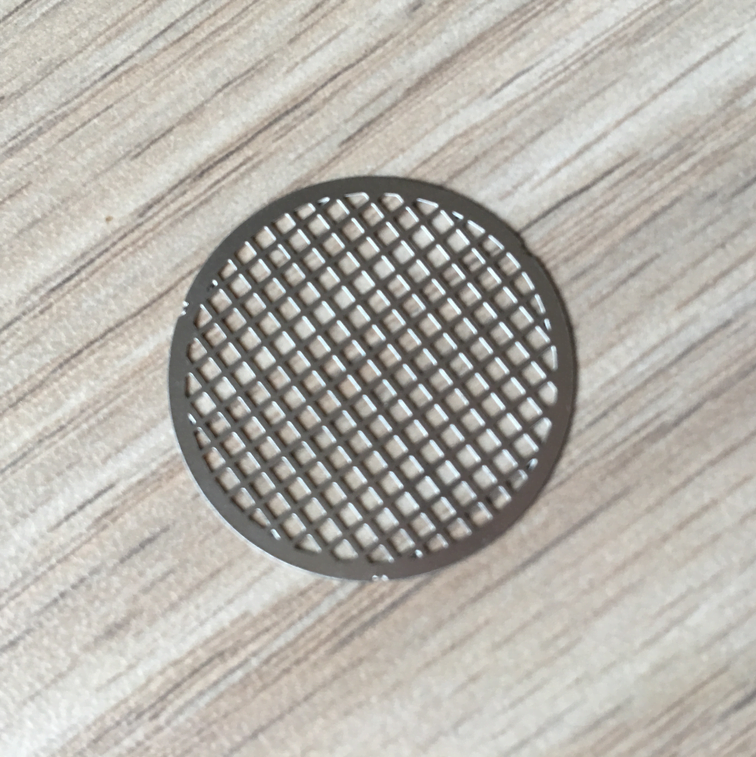
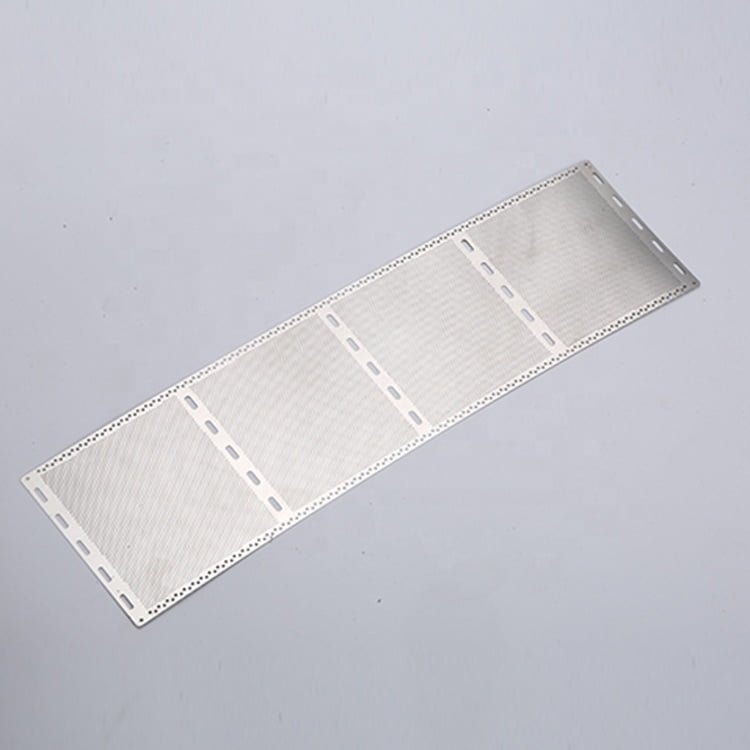
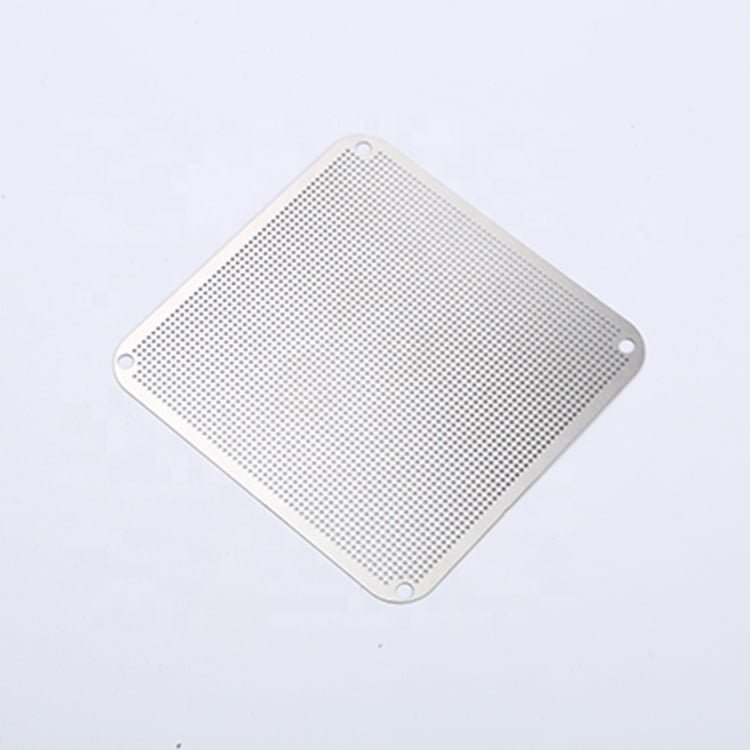
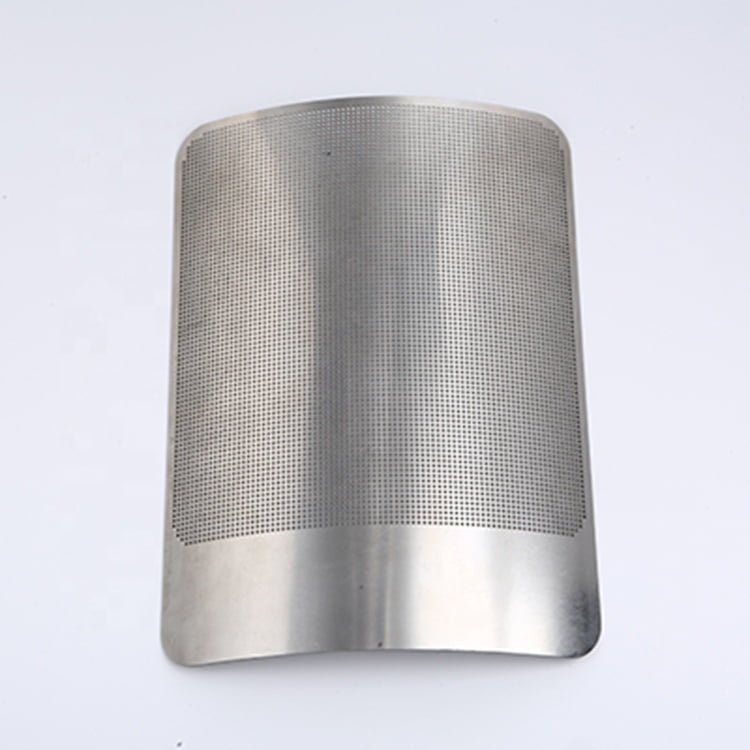
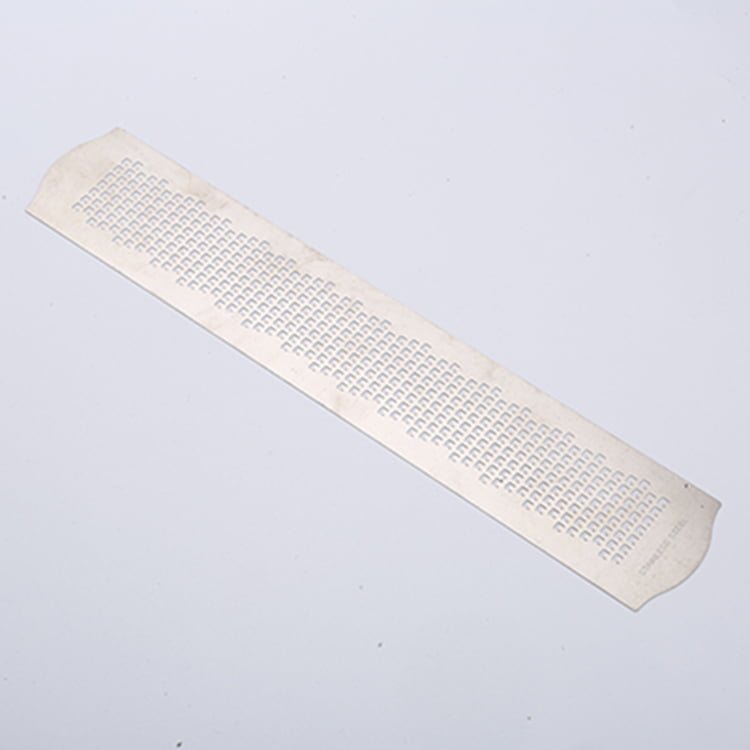
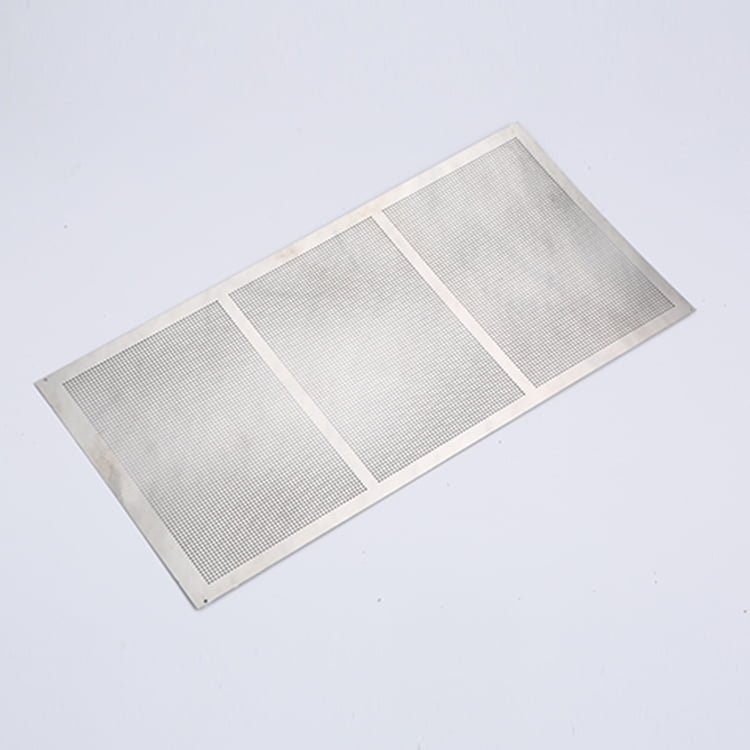
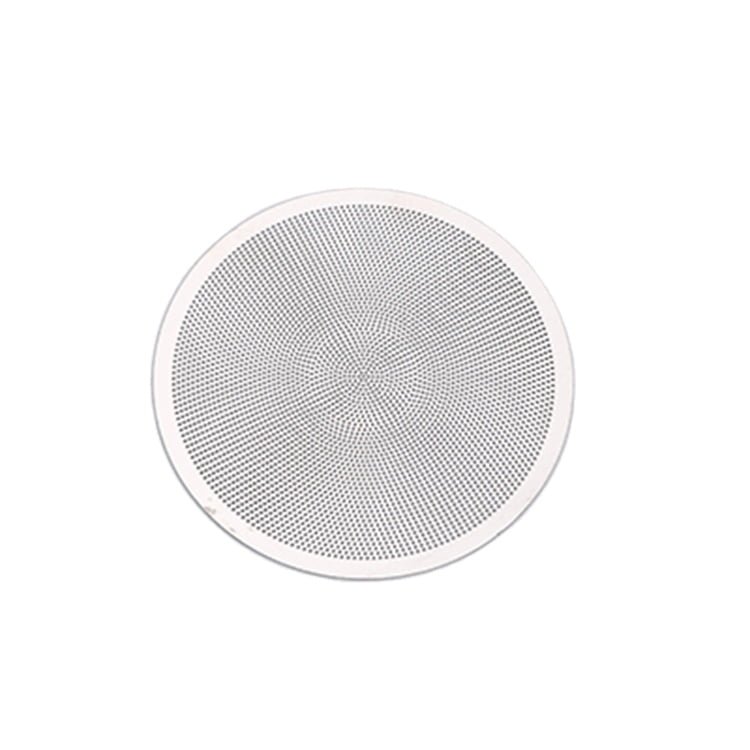
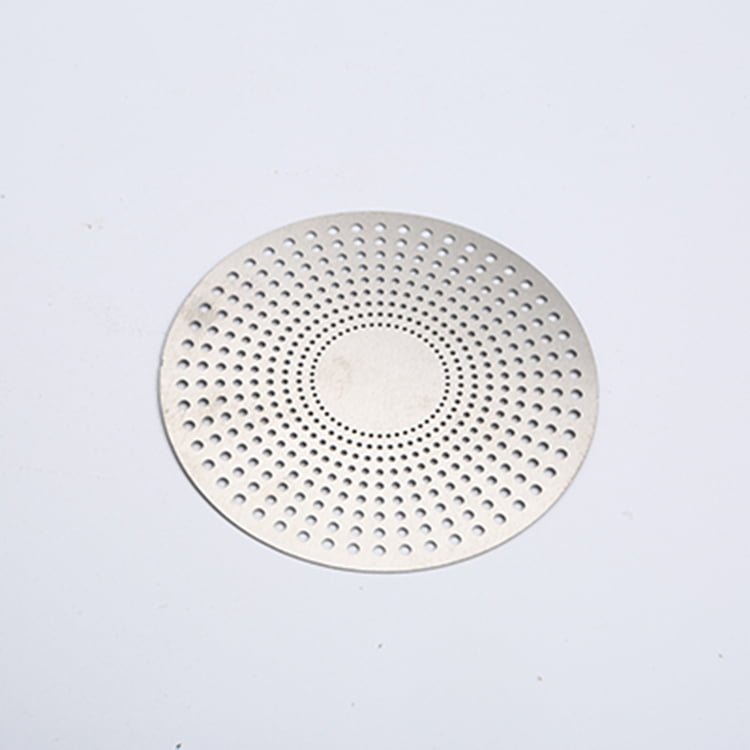
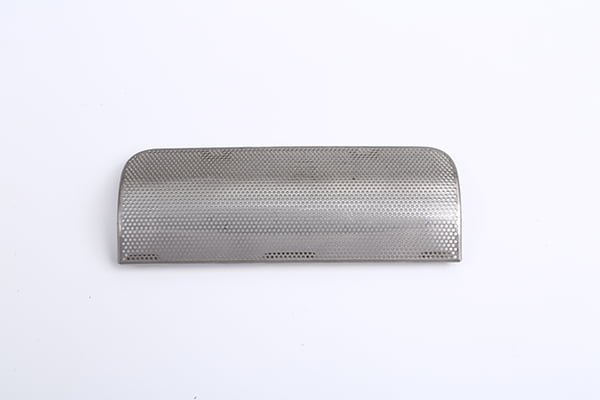
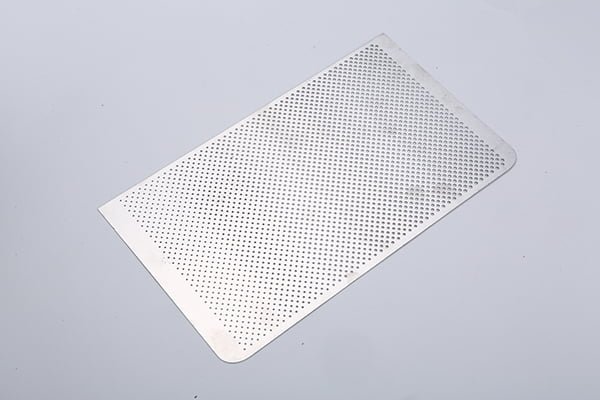
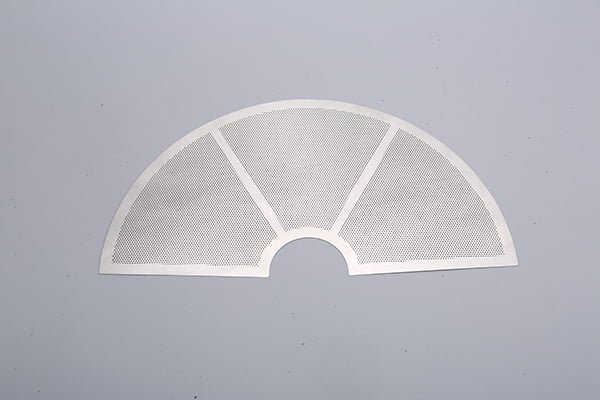
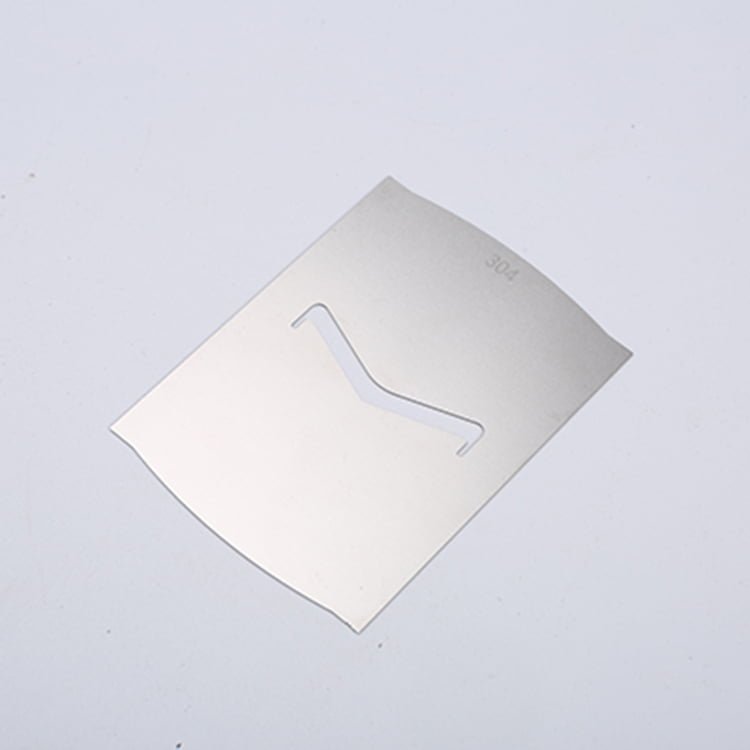
Rhenium, a rare and valuable refractory metal, has gained widespread recognition for its extraordinary properties, including an exceptionally high melting point (3,180°C/5,756°F), excellent mechanical strength, and remarkable resistance to wear and corrosion.
Our Packages
- From 1000pcs
- Samples from 100pcs
- Approx. 30 days (may vary depending on the difficulty of the drawing)
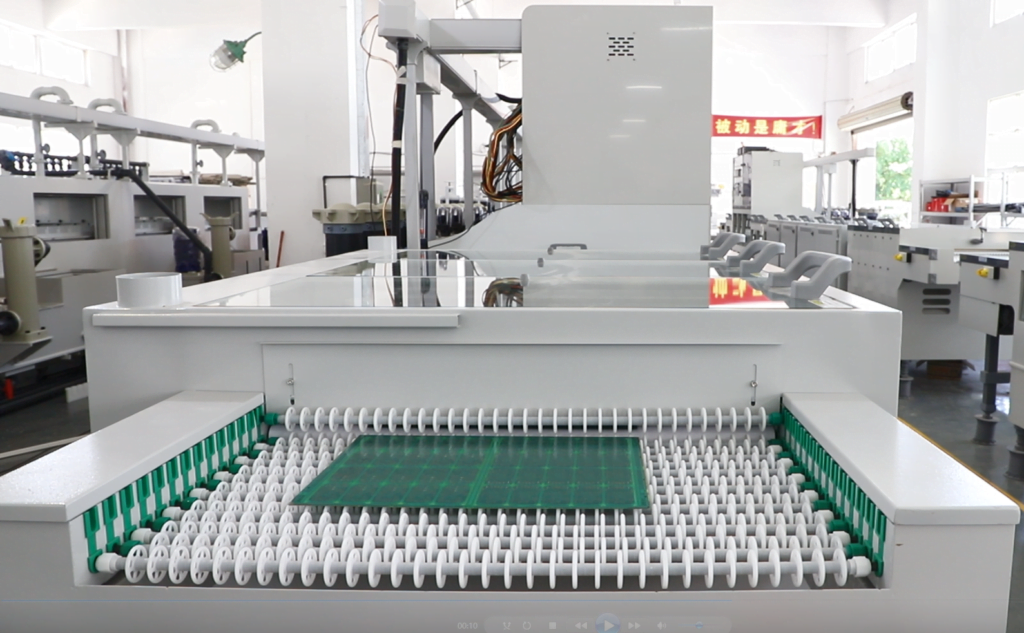
View our Rheniumetching production facility
Types of Rhenium and Alloys
Pure Rhenium (Re) is highly valued for its purity and exceptional mechanical properties, but it is often alloyed with other metals to enhance specific attributes. Some common Rhenium alloys include:
a. Rhenium-Molybdenum (Re-Mo): This alloy combines the superior ductility and formability of Molybdenum with Rhenium’s high-temperature strength and resistance to oxidation, making it ideal for applications in jet engines, rocket nozzles, and furnace components.
b. Rhenium-Tungsten (Re-W): Re-W alloys boast enhanced mechanical properties, such as increased strength and hardness, and are commonly used in aerospace and electrical applications.
c. Rhenium-Iridium (Re-Ir): The Re-Ir alloy offers improved creep resistance and high-temperature stability, making it suitable for use in thermocouples and other high-temperature measurement devices.
Metal Etching Rhenium
Metal etching is a fundamental process used to shape, pattern, or remove material from Rhenium surfaces. Wet etching, using etching machines, is commonly employed for this purpose. The selection of a suitable etchant depends on the desired results and the processing difficulty involved. Common etchants for Rhenium include:

a. Hydrofluoric Acid (HF): A highly corrosive etchant suitable for removing thin layers of Rhenium and achieving precise etching.
b. Ferric Chloride Etchant: Widely used for etching Rhenium due to its ability to create deep and well-defined patterns.
c. Cupric Chloride Etchant: Offers controlled etching and is commonly used in electronic applications.
Rhenium is a relatively rare and expensive metal, and its etching process often involves using acid-based etchants like Hydrofluoric Acid (HF) or Ferric Chloride Etchant.
Acid-based etchants are typically more effective in removing Rhenium and achieving precise etching results. Hydrofluoric Acid, in particular, is commonly used for Rhenium etching due to its high reactivity with the metal.
Rhenium etching equipment
Photo Etching Rhenium
Photo etching, also known as chemical milling, offers precise and intricate patterns on Rhenium surfaces. The process involves using light-sensitive masks to protect specific areas while etching the exposed regions. The difficulty lies in handling the photoresist and ensuring accurate pattern transfer. Skilled expertise is crucial to achieve the desired precision in the final product.

Precision-machined metal Rhenium materials are an essential component in modern technological advancements. From understanding the different types and alloys of Rhenium to navigating through the challenges of surface treatment, metal cleansing, and etching processes, manufacturers and engineers must prioritize careful selection and expertise. By doing so, they can unlock the full potential of Rhenium, utilizing its remarkable properties to revolutionize technology and engineering across diverse industries.
View our metal etching products
how to etch Rhenium?
Etching Rhenium Processing Guide
| Metal Alloy | Etchant | Temperature (°C) | Concentration (%) | Estimated Etch Depth (microns) | Etch Quality |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Etching Rhenium-M | Hydroflu | 20 | 5% | 10-30 | High-quality (smooth) |
| Etching Rhenium-Molybdenum | Ferric Chloride Etchant | 25 | 10% | 20-50 | Moderate-quality (etched) |
| Etching Rhenium-Molybdenum | Cupric Chloride Etchant | 30 | 15% | 30-70 | Low-quality (rough) |
| Etching Rhenium-Tungsten | Hydrofluoric Acid (HF) | 20 | 5% | 12-35 | High-quality (smooth) |
| Etching Rhenium-Tungsten | Ferric Chloride Etchant | 25 | 10% | 25-60 | Moderate-quality (etched) |
| Etching Rhenium-Tungsten | Cupric Chloride Etchant | 30 | 15% | 40-90 | Low-quality (rough) |
| Etching Rhenium-Iridium | Hydrofluoric Acid (HF) | 20 | 5% | 15-40 | High-quality (smooth) |
| Etching Rhenium-Iridium | Ferric Chloride Etchant | 25 | 10% | 30-75 | Moderate-quality (etched) |
| Etching Rhenium-Iridium | Cupric Chloride Etchant | 30 | 15% | 50-110 | Low-quality (rough) |
Please note that the estimated etch depths and etch quality may vary based on factors such as exposure time, surface condition, and specific etching conditions. Always conduct test etches and adjust parameters as needed to achieve your desired results. Additionally, safety precautions should be followed when handling these chemicals.
If you have metal wet etching Rhenium needs, please feel free to contact us.
FAQs
What metals can you use to customize my goods?
- Wet Etching Germanium
- Wet Etching Gallium Nitride (GaN)
- Wet Etching Indium
- Wet Etching Cobalt
- Wet Etching Tungsten
- Wet Etching Stainless Steel
- Wet Etching Aluminum
- Wet Etching Kovar
- Wet Etching Copper
- Wet Etching Steel
- Wet Etching Nickel
- Wet Etching Platinum
- Wet Etching Silver
- Wet Etching Rhodium
- Wet Etching Hafnium
- Wet Etching Vanadium
- Wet Etching Zirconium
- Wet Etching Titanium
- Wet Etching Niobium
- Wet Etching Tantalum
- Wet Etching Molybdenum
- Wet Etching Brass
- Wet Etching Rhenium
How quickly can I get your response?
Within 24 hours.
Will you do 100% inspection before shipping out the orders?
Yes we do.
Can I have prototypes or samples before placing the order?
Samples are always available.
Etching Rhenium Samples